The World of Living refers to the study of living organisms, including plants and animals, and their interactions with each other and with their environment. It is a broad field of study that encompasses many different disciplines, such as biology, ecology, and environmental science.
At the Class 10 level, students may study topics such as:
- The characteristics of living organisms
- The classification of living organisms
- The structure and function of cells
- The process of photosynthesis
- The human body and it’s systems
- The ecology of different environments
- The impact of human activity on the environment
This subject can also include topics like the conservation of biodiversity, genetic engineering and biotechnology, human impact on the environment, and the study of microorganisms, fungi, and protozoa.
Understanding the World of Living is important because it helps us understand the intricacies and interdependence of the natural world and how humans affect it. By studying the diversity of life and how organisms interact with one another and their environment, we can gain insight into the relationships that sustain life on Earth, and how to protect and preserve it for future generations.
This unit consists of 4 chapters:
- Life processes —> Click Here for Notes
- Control and coordination in animals and plants —> Click Here for Notes
- How do organisms reproduce?
- Heredity and evolution
The living world important notes
Q. what are the characteristics of living organisms?
Ans: The characteristics of living organisms are stated below:
- Organization: All living organisms are composed of cells, which are the basic unit of life. These cells are organized into tissues, which are organized into organs, and then into systems.
- Metabolism: Living organisms have the ability to carry out chemical reactions to maintain their life processes. These reactions can be either anabolic (building up) or catabolic (breaking down).
- Growth and Development: Living organisms grow and develop over time. This can include physical growth, such as an increase in size, or developmental growth, such as the development of new skills or abilities.
- Response to Stimuli: Living organisms are able to respond to changes in their environment. This can include things like moving towards or away from light, or responding to changes in temperature.
- Reproduction: Living organisms have the ability to reproduce, either sexually or asexually. This allows for the continuation of the species.
- Homeostasis: Living organisms maintain a stable internal environment, despite changes in the external environment. This is known as homeostasis.
- Adaptation: Living organisms are able to adapt to changes in their environment in order to survive. This can include physical adaptations, such as changes in body shape or color, or behavioral adaptations, such as changes in feeding or mating habits.
- Evolution: Living organisms change over time through the process of evolution. This can include changes in physical characteristics, behavior, or genetics.
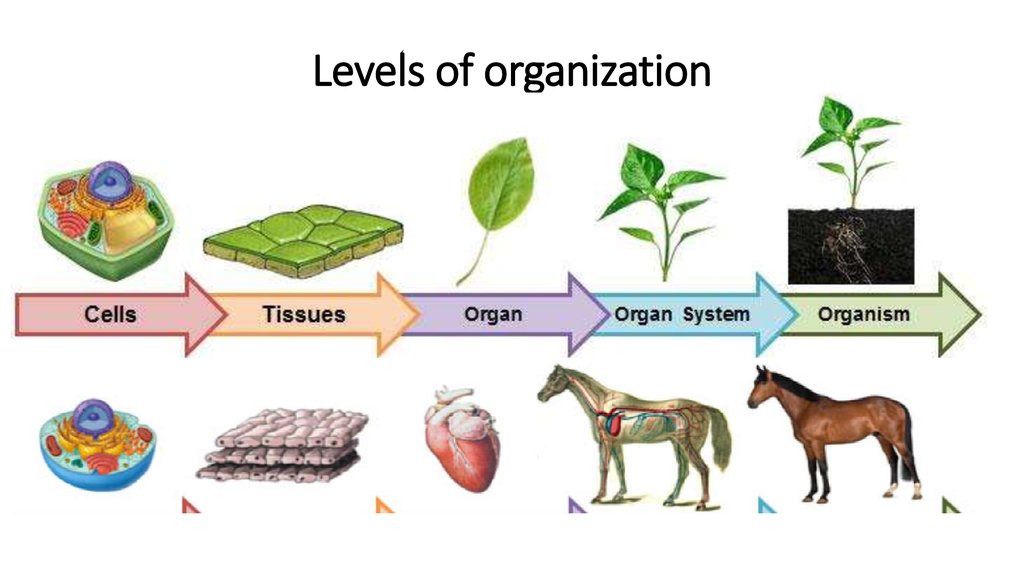
Q. What are the levels of organization in living things?
Ans: Below are the key terms that describe the levels of organization in living things:
- Cellular level: The smallest unit of living organisms is the cell. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- Tissue level: Groups of similar cells that perform a specific function make up tissues. For example, muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and epithelial tissue.
- Organ level: Organs are made up of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. For example, the heart, lungs, and liver.
- Organ system level: Organ systems are made up of different organs that work together to perform a specific function. For example, the circulatory system, the digestive system, and the respiratory system.
- Organism level: An organism is a single living being, such as a human, a dog, or a tree. It is made up of different organ systems that work together to keep the organism alive.
- Population-level: A population is a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area at the same time.
- Community level: A community is made up of different populations of different species that live in the same area at the same time.
- Ecosystem level: An ecosystem is made up of different communities of living and non-living things that interact with each other in a specific area.
- Biosphere level: The biosphere is the part of the Earth that is inhabited by life. It includes all the ecosystems on the planet, from the depths of the oceans to the tops of the mountains.
Each level of organization is dependent on the one below it and together they form a complex system that allows living organisms to survive and evolve.
Q. What are the functions of different organ systems in the human body?
Ans: The different organ systems in the human body have specific functions that help to keep the body functioning properly. These include:
- The skeletal system: This system provides support and protection for the body. It also allows for movement through the attachment of muscles to bones.
- The muscular system: This system allows for movement, as well as maintaining posture and generating heat.
- The nervous system: This system controls and coordinates the body’s response to internal and external stimuli. It also controls the functions of other organ systems, such as the heart and lungs.
- The cardiovascular system: This system circulates blood throughout the body, bringing oxygen and nutrients to the cells and removing waste products.
- The respiratory system: This system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide.
- The digestive system: This system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients, which are then transported to the cells.
- The urinary system: This system removes waste products and excess water from the body.
- The reproductive system: This system produces gametes and allows for the reproduction of the species.
- The endocrine system: This system secretes hormones that control the body’s growth, metabolism, and response to stress and other external changes.
- The immune system: This system helps protect the body from disease and infection by identifying and eliminating foreign substances.
All these organ systems work together to maintain the body’s internal environment, respond to external stimuli, and keep the body alive.

Q. Photosynthesis | Definition, Formula, Process, Diagram
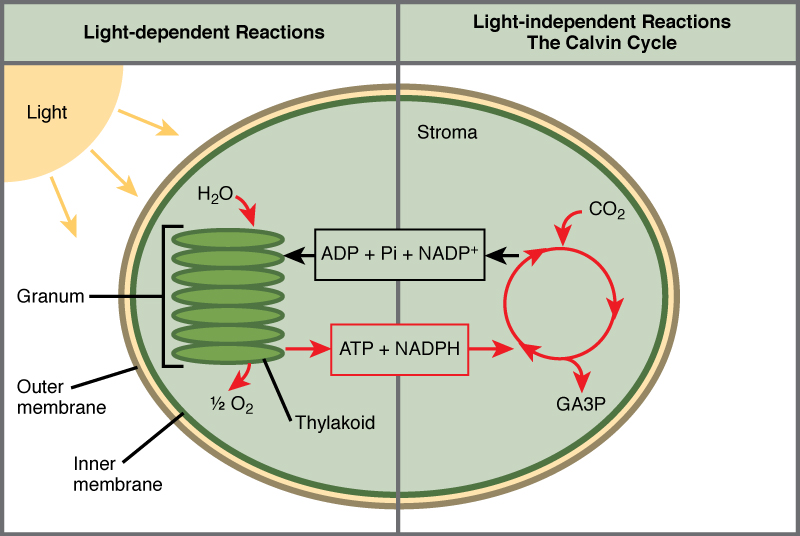
Ans: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae and some microorganisms convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (a sugar) and other organic compounds. The process of photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle).
Light-dependent reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts. They convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The light energy is absorbed by pigments, mainly chlorophyll, which excites electrons, these electrons are then used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient that is used to generate ATP and NADPH through chemiosmosis.
Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts. They use the energy from ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose and other organic compounds. This process is known as carbon fixation, and it involves a series of chemical reactions that are catalyzed by enzymes. These reactions form a cycle, and it is called the Calvin cycle.
In summary, the process of photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the air as a byproduct of the process, while the glucose is used by the plant as an energy source.
Q. Respiration- Types and Phases Of Respiration In Organisms
Ans: Respiration is the process by which living organisms convert the chemical energy stored in organic molecules (such as glucose) into a form that can be used by the cells to perform work. It can be divided into two main stages: cellular respiration and breathing (respiration in the lungs).
- Cellular Respiration: This is the process that occurs within the cells of an organism. The primary goal of cellular respiration is to convert glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the process. This energy is stored in the form of ATP, which can be used by the cells for various functions.
The process of cellular respiration can be further divided into three stages: - Glycolysis: This occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the breakdown of one glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, releasing energy in the form of ATP and NADH.
- Krebs cycle (Citric acid cycle): This occurs in the mitochondria and involves the conversion of pyruvate into CO2, releasing energy in the form of ATP and NADH.
- Electron Transport Chain: This occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, releasing energy in the form of ATP.
- Breathing: This is the process of exchanging gases (O2 and CO2) between the body and the environment. In mammals and birds, it occurs in the lungs, where oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is expelled. During inspiration, the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, expanding the thoracic cavity, and allowing air to flow into the lungs. During expiration, these muscles relax, and the air flows out of the lungs.
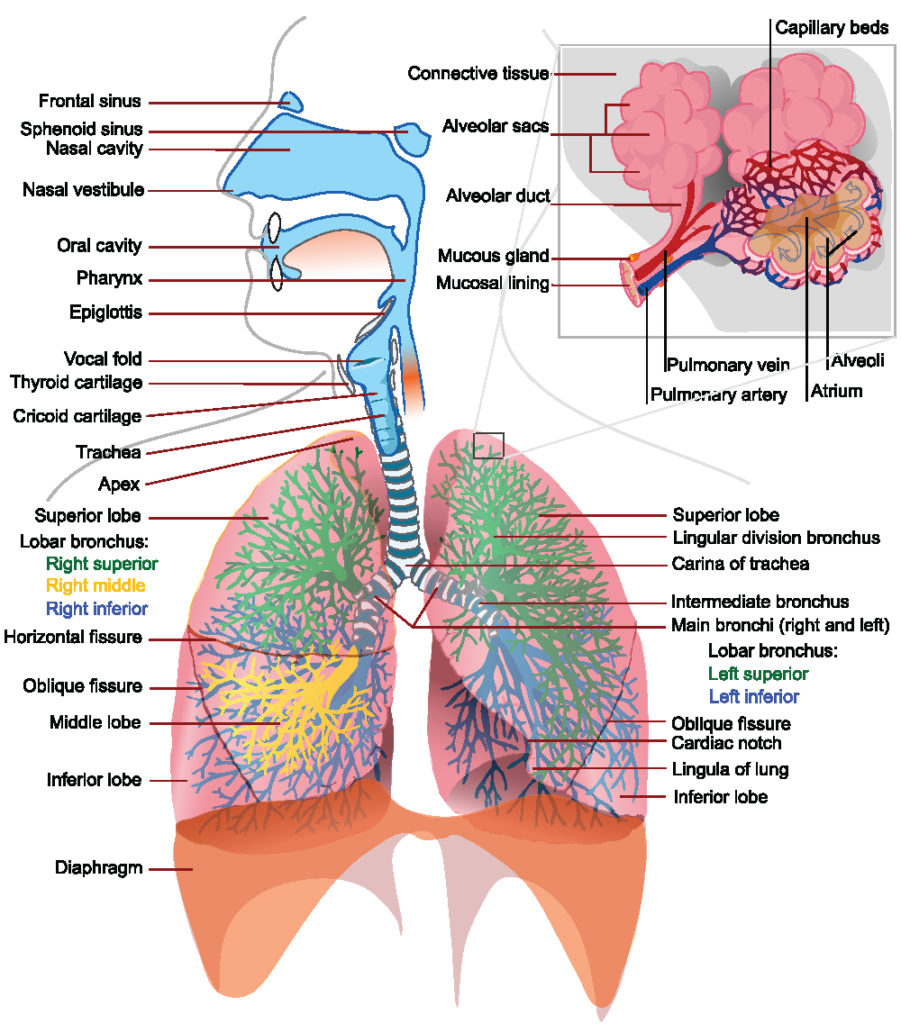
In summary, the process of respiration involves the conversion of glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the form of ATP. This process occurs in two stages: cellular respiration within the cells and breathing (exchange of gases) in the lungs or other organs.
Q. The various modes of reproduction in living organisms
Ans: There are several different modes of reproduction in living organisms, which can be broadly classified into two categories:
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
1. Asexual reproduction: This is a mode of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes. Some examples of asexual reproduction include:
I. Binary fission: This is the process by which a single organism divides into two identical offspring. It is commonly seen in bacteria and protists.
II. Fragmentation: This is the process by which an organism breaks apart into multiple pieces, each of which can grow into a new organism. It is commonly seen in sponges, corals, and some worms.
III. Vegetative reproduction: This is the process by which new plants are produced from vegetative parts of the parent plant, such as the roots, stem, or leaves. Examples include bulbs, runners, and tubers.
2. Sexual reproduction: This is a mode of reproduction that involves the fusion of gametes, which are specialized cells that carry genetic information. Some examples of sexual reproduction include:
I. Fertilization: This is the process by which the sperm and egg fuse to form a zygote. It is commonly seen in animals and plants.
II. Meiosis: This is the process by which the number of chromosomes in the reproductive cells is reduced by half. This is necessary to ensure that the offspring have the correct number of chromosomes.
Both modes of reproduction have their advantages and disadvantages. Asexual reproduction allows for the rapid production of large numbers of offspring, but it also increases the likelihood of genetic disorders. Sexual reproduction allows for greater genetic diversity, but it also slows down the production of offspring.
Q. The concept of heredity and how traits are passed down from parents to offspring
Ans: Heredity is the concept of how traits or characteristics are passed down from parents to their offspring. The study of heredity is called genetics. Traits are determined by genes, which are segments of DNA that carry the instructions for the development of specific characteristics.
Each organism has a set of chromosomes, which are long strings of DNA that carry genetic information. Chromosomes come in pairs, with one copy inherited from each parent. Each chromosome carries many genes, which are specific segments of DNA that contain the instructions for the development of a particular trait.
During reproduction, the chromosomes from the parents are combined in the offspring. This process is called meiosis. During meiosis, the chromosomes of the parent cells are replicated and then split, resulting in the formation of four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells. These cells are called gametes, and they come together during fertilization to form a new organism.
When the gametes combine, each gene on a chromosome can come from either the mother or the father, and the combination of these genes determines the trait of the offspring. The specific combination of genes that an organism inherits is called its genotype, while the observable traits that result from the genotype are called its phenotype.
Q. The theory of evolution and the evidence for it
Ans: The theory of evolution is the scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth and the changes that have occurred over time. It was first proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in the mid-19th century, and it is widely accepted by the scientific community. The theory of evolution proposes that all living organisms have a common ancestor and have changed over time through the process of natural selection.
The central idea of the theory of evolution is that over time, certain traits that are advantageous to an organism’s survival and reproduction will become more common in a population. This is known as natural selection. Organisms with traits that are not advantageous will be less likely to survive and reproduce, and their traits will become less common in the population. Over many generations, this process can lead to the evolution of new species.
There are many lines of evidence that support the theory of evolution. Some of the most important are:
Fossil record: Fossils are the remains of ancient organisms that have been preserved in rock. The fossil record provides evidence of the existence of extinct species and the gradual changes that have occurred in the forms of life over time.
Comparative anatomy and physiology: The study of the structures and functions of different organisms’ body parts reveals similarities and differences between different species. These similarities and differences provide evidence of the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Biogeography: The study of the distribution of different species on the Earth provides evidence of the evolutionary relationships between different species and the changes that have occurred in the Earth’s environment over time.
Molecular biology: The study of the genetic makeup of different species provides evidence of the evolutionary relationships between different species and the changes that have occurred in the genetic makeup of different species over time.
We have provided the best notes for all these above chapters with the best class 10 science chapter-wise questions and answers. Apart from this, we provide free video lectures for all the class 10 science notes unit-wise. For videos or lectures go to youtube and search Academic Excellence in Schools and search for the particular playlists.
Click Here for the important MCQs for World of Living class 10 chapter-wise: Class 10 MCQs Practice for Free
If you have any queries or doubts about any topics of class 10 science, feel free to write a comment below. Our expert teacher will answer your questions shortly.
